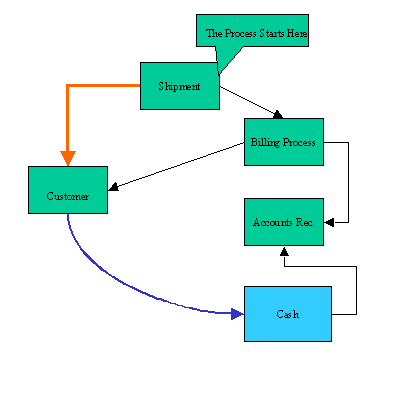
The Accounts Receivable process starts with the shipment of the goods to the customer. When this occurs, the shipping department automatically causes SAP to send a bill to the customer by integrating customer master data with the shipment data. This transaction also posts to the Accounts Receivable subsidiary ledger and also to the reconciliation account. The billing to the customer may be on paper or by EDI.
This entry into the accounts receivable system sets up the account for the terms of sale and also starts the clock running for the dunning procedure.
When the customer pays the bill, which may be by check or to a lockbox or by electronic transfer and EDI, the remittance advice applies the cash paid to the open items on the account.
Some important concepts:
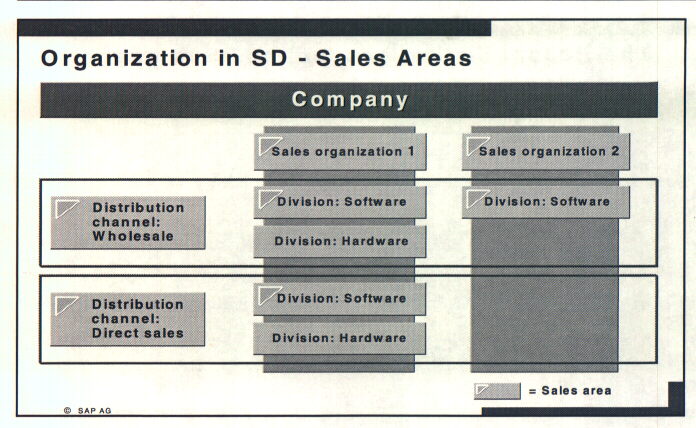
Sales Areas: A sales area is a combination of sales organization, distribution channel and division.
The Reconciliation Account and Subledgers:

The Purpose and Operation of the Reconciliation Account
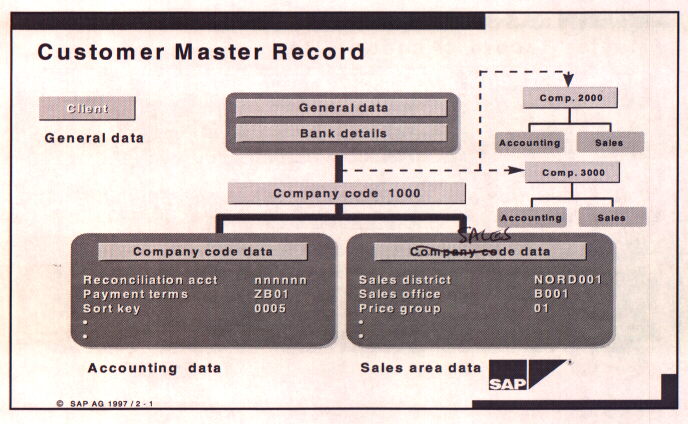
The concept of master data is an important one in data management. Although it may seem complex at first glance it is the best method to eliminate duplication of data and to ensure compatibility of data among transactions. Every customer has master data associated with it. It is defined only once and in only one location, although there is a hierarchy of where that data is stored.
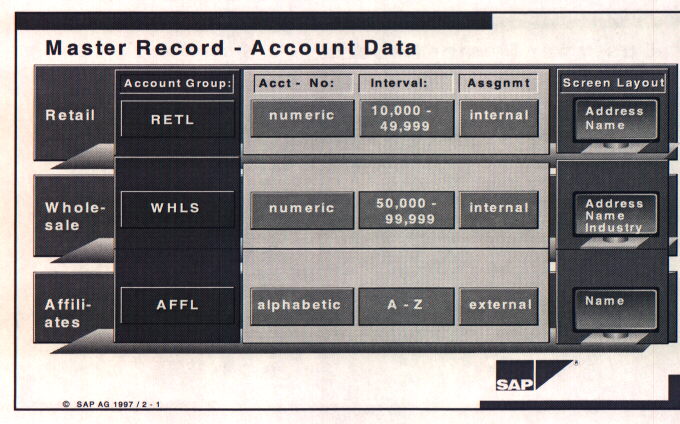
Account Groups:

Address and Communications:
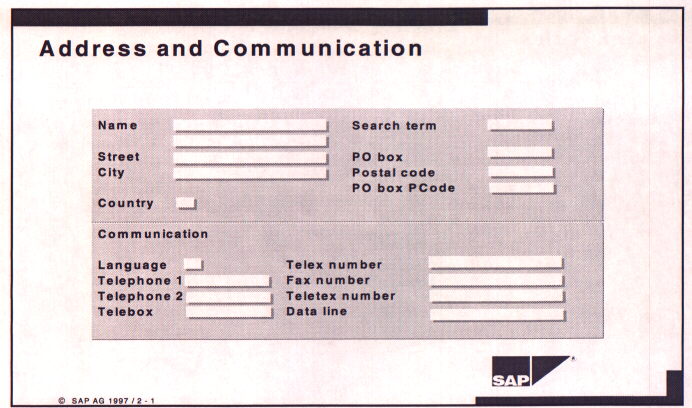
On the first screen of the customer master record basic data on the customer is listed. This includes addresses and important numbers for communication. This data is entered at the client level. Additional information can also be entered at the company code level. To prevent a customer from being created twice in your system, you need to determine who in your organization is responsible for creating new customers. Initial contact with a new customer will probably be made by the Sales Organization and the master record will need to be completed by the accounting and finance functions.
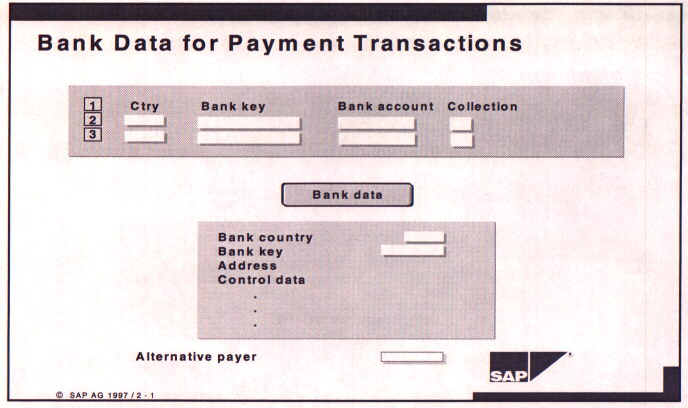
Bank master data includes the following items to facilitate payments to or
from the customer by check or EDI.
Account Management and Reconciliation Account
On the next screen of the master record you store the information that is relevant to accounting at the company code level. This is a critical link between the sales data and the general ledger systems.

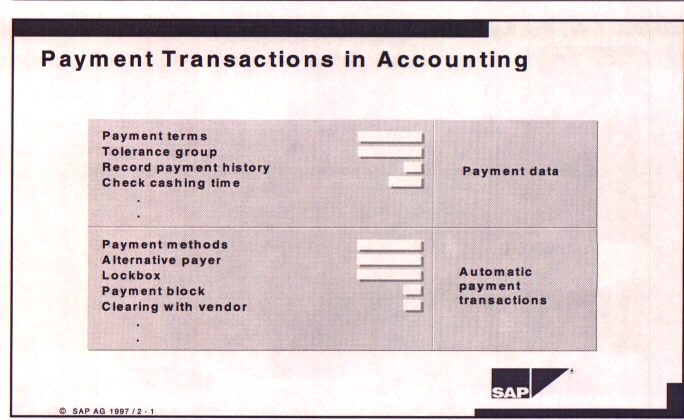
Payment Transaction Data:
The following screen sets the parameters for the accounts receivable administration of the customer. Payment term groups are defined in the IMG and are assigned to this account. Likewise, tolerance limits for over and under payments of items are defined in the IMG and assigned to the account. The days specified for check cashing time are inmportant for the treasury and cash management modules. There are also fields for payment methods and lockbox codes which have been defined in the IMG and assigned to this account.
Dunning Data:
The next screen shows the entries for setting up dunning for the account.

Summary: Creating and maintaining customer master records are of critical importance in SAP. New customer masters can be created by using a reference from another account and simply changing the relevant data. Much of the data can be automatically filled in by a pattern created by a Group key which can be selected at the beginning of the generation process.