Performance Evaluation Tests
The success of the training program is largely dependent upon satisfying the performance aims associated with it.
How can performance be monitored?
Testing and measurement are the means of collecting information upon which subsequent performance evaluations and decisions are made.
Cooper VO2max Test
Objective
To monitor the development of the athlete's general endurance.
Required Resources
To undertake this test you will require:
- 400 meter track - marked every 100 meters
- Stop watch
- Assistant
How to conduct the test
The test comprises of seeing how far an athlete can run/walk in twelve minutes. The assistant should record the total distance covered to the nearest 100 meters.
Analysis
Analysis of the result is by comparing it with the results of previous tests. It is expected that, with appropriate training between each test, the analysis would indicate an improvement.
Performance Assessment
For an evaluation of the athlete's performance select the age group and gender, enter the total distance covered and then select the 'Calculate' button.
Normative data for the Cooper Test
Age |
Excellent |
Above Average |
Average |
Below Average |
Poor |
Male 13-14 |
>2700m |
2400-2700m |
2200-2399m |
2100-2199m |
<2100m |
Males 15-16 |
>2800m |
2500-2800m |
2300-2499m |
2200-2299m |
<2200m |
Males 17-19 |
>3000m |
2700-3000m |
2500-2699m |
2300-2499m |
<2300m |
The following table rates performance for athletes:
Age |
Excellent |
Above Average |
Average |
Below Average |
Poor |
Male 20-29 |
>2800m |
2400-2800m |
2200-2399m |
1600-2199m |
<1600m |
Males 30-39 |
>2700m |
2300-2700m |
1900-2299m |
1500-1999m |
<1500m |
Males 40-49 |
>2500m |
2100-2500m |
1700-2099m |
1400-1699m |
<1400m |
Males >50 |
>2400m |
2000-2400m |
1600-1999m |
1300-1599m |
<1300m |
Home Step Test:
Objective
The objective of this test is to monitor the development of the athlete's cardiovascular system.
Required Resources
To undertake this test you will require:
- A 12 inch high bench or step
- A stop watch
- Metronome or cadence tape
- An assistant
How to conduct the test
The Home Step Test is conducted as follows:
- Step up and down, one foot at a time, onto the step or bench for 3 minutes
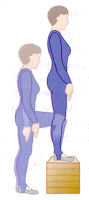
- Try to maintain a steady four beat cycle (approx. 22 to 24 steps/minute)
- Use a metronome or have someone to help you keep to the required pace
- On finishing the test count the number of heart beats for 15 seconds
- Multiply the number of beats in 15 seconds by 4
- Use this final value to assess your performance using the appropriate table below
Analysis
Analysis of the result is by comparing it with the results of previous tests. It is expected that, with appropriate training between each test, the analysis would indicate an improvement. Top of Form
Performance Assessment
For an evaluation of the athlete's performance select the age group and gender, enter the number of beats in 60 seconds and then select the 'Calculate' button.
Male athletes:
Age |
18-25 |
26-35 |
36-45 |
46-55 |
56-65 |
65+ |
Excellent |
<79 |
<81 |
<83 |
<87 |
<86 |
<88 |
Good |
79-89 |
81-89 |
83-96 |
87-97 |
86-97 |
88-96 |
Above Average |
90-99 |
90-99 |
97-103 |
98-105 |
98-103 |
97-103 |
Average |
100-105 |
100-107 |
104-112 |
106-116 |
104-112 |
104-113 |
Below Average |
106-116 |
108-117 |
113-119 |
117-122 |
113-120 |
114-120 |
Poor |
117-128 |
118-128 |
120-130 |
123-132 |
121-129 |
121-130 |
Very Poor |
>128 |
>128 |
>130 |
>132 |
>129 |
>130 |
Table Reference: Canadian Public Health Association
Illinois Agility Run Test
Objective
The objective of the Illinois Agility Run Test is to monitor the development of the athlete's agility.
- flat surface - a 400 metre Track
- 8 cones
- Stop watch
- Assistant
The Illinois course
The length of the course is 10 metres and the width (distance between the start and finish points) is 5 metres. On an athletics track, you could use 5 lanes.
4 cones can be used to mark the start, finish and the two turning points. Each cone in the centre is spaced 3.3 metres apart.
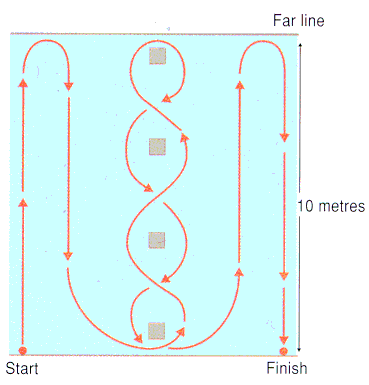
How to conduct the test
The Illinois Agility Run Test is conducted as follows:
- The athlete lies face down on the floor at the start point
- On the assistant's command the athlete jumps to his/her feet and negotiates the course around the cones to the finish
- The assistant records the total time taken from their command to the athlete completing the course.
Analysis
Analysis of the result is by comparing it with the results of previous tests. It is expected that, with appropriate training between each test, the analysis would indicate an improvement.
The following are national norms for 16 to 19 year olds.
Gender |
Excellent |
Above Average |
Average |
Below Average |
Poor |
Male |
<15.2 secs |
15.2 - 16.1 secs |
16.2 - 18.1 secs |
18.2 - 18.3 secs |
>18.3 secs |
Female |
<17.0 secs |
17.0 - 17.9 secs |
18.0 - 21.7 secs |
21.8 - 23.0 secs |
>23.0 secs |
Table Reference: Davis B. et al; Physical Education and the Study of Sport; 2000
Sit & Reach Test:
Objective
The objective of this test is to monitor the development of the athlete's lower back and hamstring flexibility.
Objective
The objective of this test is to monitor the development of the athlete's lower back and hamstring flexibility.
Required Resources
To undertake this test you will require:
- A 'sit & reach table' or a bench with a ruler
- An assistant
How to conduct the test
The Sit and Reach Test is conducted as follows:
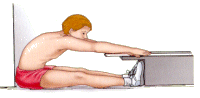 The starting position is sitting on the floor with shoes removed, feet flat against the table, and legs straight
The starting position is sitting on the floor with shoes removed, feet flat against the table, and legs straight- Reach forward and push the fingers along the table as far as possible
- The distance from the finger tips to the edge of the table represents the score for that person
- As the 'sit and reach' table has an overhang of 15 cm, a person who reaches 10 cm past their toes scores 25 cm
- It is important to have several warm-up attempts first, and to record the best score
Analysis
Analysis of the result is by comparing it with the results of previous tests. It is expected that, with appropriate training between each test, the analysis would indicate an improvement.
The following are national norms for 16 to 19 year olds.
Gender |
Excellent |
Above average |
Average |
Below average |
Poor |
Male |
>14 |
11 - 14 |
7 - 10 |
4 - 6 |
<4 |
Female |
>15 |
12 - 15 |
7 - 11 |
4 - 6 |
<4 |
Table Reference: Davis B. et al; Physical Education and the Study of Sport; 2000
Curl-Up Test
Objective
The objective of the Curl-Up Test is to assess the endurance of the athlete's abdominal muscles.
Objective
The objective of the Curl-Up Test is to assess the endurance of the athlete's abdominal muscles.
Required Resources
To undertake this test you will require:
- flat surface
- mat
- watch
- a partner
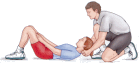
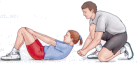
How to conduct the testThe Sit Ups Test is conducted as follows:
|
|
Analysis
Analysis of the result is by comparing it with the results of previous tests. It is expected that, with appropriate training between each test, the analysis would indicate an improvement.
The following table is for Male athletes.
Classification |
<35 |
35 - 44 |
>45 |
Excellent |
60 |
50 |
40 |
Good |
45 |
40 |
25 |
Fair |
30 |
25 |
15 |
Poor |
15 |
10 |
5 |
Table Reference: McArdle W.D. et al; Essential of Exercise Physiology; 2000
Sit Ups Test.
Objective
The objective of the Sit Ups Test is to monitor the development of the athlete's abdominal muscles.
Required Resources
To undertake this test you will require:
- flat surface
- mat
- a partner to hold the feet
How to conduct the test
The Sit Ups Test is conducted as follows:
- Lie on the mat with the knees bent, feet flat on the floor and the arms folded across the chest
- Start each sit up with back on the floor.
- Raise yourself to the 90 degree position and then return to the floor
- The feet can be held by a partner
- Record the number of sits up completed in 30 seconds
Analysis
Analysis of the result is by comparing it with the results of previous tests. It is expected that, with appropriate training between each test, the analysis would indicate an improvement.
The following are national norms for 16 to 19 year olds.
Gender |
Excellent |
Above Average |
Average |
Below Average |
Poor |
Male |
>30 |
26 - 30 |
20 - 25 |
17 - 19 |
<17 |
Female |
>25 |
21 - 25 |
15 - 20 |
9 - 14 |
<9 |
Table Reference: Davis B. et al; Physical Education and the Study of Sport; 2000
Press-Up Test.
Objective
The objective of the Press Up test is to assess the endurance of the athlete's upper body muscles.
Required Resources
To undertake this test you will require:
- flat surface
- mat
- a partner
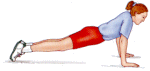
How to conduct the testThe Press Up Test is conducted as follows:
|
|
Female athletes tend to have less relative strength in the upper body and therefore can use the modified press up position to assess their upper body strength. The test is then performed as follows:
|
|
Analysis
Analysis of the result is by comparing it with the results of previous tests. It is expected that, with appropriate training between each test, the analysis would indicate an improvement.
Full body press up
Age |
|||||
Excellent |
Good |
Average |
Fair |
Poor |
|
20 - 29 |
>54 |
45 – 54 |
35 - 44 |
20 - 34 |
<20 |
30 - 39 |
>44 |
35 – 44 |
25 - 34 |
15 - 24 |
<15 |
40 -49 |
>39 |
30 – 39 |
20 - 29 |
12 - 19 |
<12 |
50 - 59 |
>34 |
25 – 34 |
15 - 24 |
8 - 14 |
<8 |
60+ |
>29 |
20 – 29 |
10 - 19 |
5 - 9 |
<5 |
Modified Push Ups
Age |
Excellent |
Good |
Average |
Fair |
Poor |
20 - 29 |
>48 |
34 - 38 |
17 - 33 |
6 - 16 |
<6 |
30 - 39 |
>39 |
25 - 39 |
12 - 24 |
4 - 11 |
<4 |
40 -49 |
>34 |
20 - 34 |
8 - 19 |
3 - 7 |
<3 |
50 - 59 |
>29 |
15 - 29 |
6 - 14 |
2 - 5 |
<2 |
60+ |
>19 |
5 – 19 |
3 - 4 |
1- 2 |
<1 |
Table Reference: McArdle W.D. et al; Essential of Exercise Physiology; 2000
Sergeant Jump Test
Objective
To monitor the development of the athlete's elastic leg strength.
Required Resources
To undertake this test you will require:
- A wall
- 1 metre Tape Measure
- Chalk
- An assistant
How to conduct the test
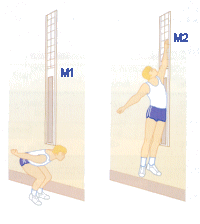
The athlete:
The coach then measures the distance from M1 to M2. The test can be performed as many times as the athlete wishes. |
|
Analysis
Analysis of the result is by comparing it with the results of previous tests. It is expected that, with appropriate training between each test, the analysis would indicate an improvement.