ICS 103: Computer Programming in C
Handout-13
Topic: 1-D
Array
(How to use
array with function)
Instructor:
M. Waheed Aslam.
Objectives:
·
Learn how to use one-dimensional arrays
with function.
·
To know how to pass individual 1-D array
elements to function.
·
To know how to pass whole 1-D array to the
function.
Using Arrays with Functions:
How to use individual array elements as parameters in function?
·
This is similar to passing simple arguments
·
The formal
parameter should be a simple variable
·
The actual parameter should be the array
name followed by the particular index in [].
Solved Problem# 1:
/***************************************************************
Write a program to find the sum of the first
three elements in an array, by passing individual array elements to the
following function.
****************************************************************/
#include<stdio.h>
int sum_elements(int
a , int b, int c); // Function Prototype
void
main()
int
x[10], total;
x[0]=10;
x[1]=20;
x[2]=30;
total
= sum_elements( x[0], x[1], x[2] ); //Function call to compute sum
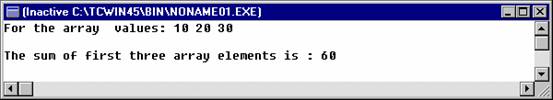
printf("For
the array values: %d %d %d\n",
x[0], x[1], x[2] );
// Output
results
printf("\nthe
sum of first three array elements is : %d", total);
}
// end of main
int sum_elements( int a, int b, int c )
// Function header
{
int
sum;
sum=a+b+c;
return
(sum);
}
Sample Output:
/*******************************************************
Another Solution of Problem #1
*******************************************************/
#include<stdio.h>
int
sum_elements(int a , int b, int c); // Function
Prototype
void
main()
{
int
x[10], total=0, i;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
scanf("%d",
&x[i]);
}
total
= sum_elements( x[0], x[1], x[2] ); //Function call
to compute sum
//
Output results
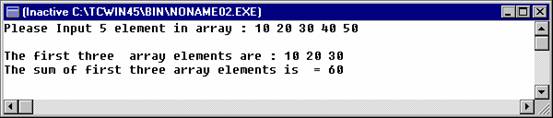
printf("\nThe
first three array elements are : %d %d
%d", x[0], x[1], x[2] );
printf("\nThe
sum of first three array elements is =
%d", total);
}
// end of main
int
sum_elements(int a, int b, int c) // Function header
{
int
sum;
sum=a+b+c;
return
(sum);
}
Sample Output:
Solved Problem #2:
//reads a 1-D array and prints the sum of even and odd
numbers
#include
<stdio.h>
#define
SIZE 4
/* determines if an element is odd */
int odd(int
num)
int isodd;
isodd = (num%2==1);
return isodd;
}
//end of odd function
int main( )
{
int x[SIZE], i, oddsum=0, evensum=0;
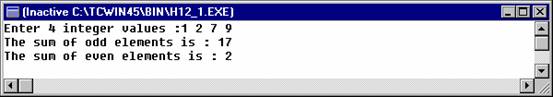
printf("Enter %d integer values :",
SIZE);
for (i=0; i<SIZE; i++)
{
}
for (i=0; i<SIZE; i++)
{
if ( odd(x[i]) ) // function call is with in if
oddsum=oddsum+x[i];
else
evensum=evensum+x[i];
}
printf("The sum of odd elements is :
%d\n", oddsum);
printf("The sum of even elements is :
%d\n", evensum);
return 0;
}
// end of main
Sample Output:
How to pass whole array as a parameter in Function?
·
Unlike simple variables,
array is not passed into a function, but rather its address is passed.
·
This is done by specifying
the array name followed by brackets [] (size is not necessary).
·
This makes processing more
efficient.
·
The actual parameter is
the array name (no brackets).
Solved Problem#3:
/* reads the grades of students and prints the average grade.*/
#include
<stdio.h>
#define
SIZE 30
/* computes the average of elements in an array */
float average(float list[], int n)
int i;
float sum=0.0;
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
sum+=list[i];
return sum/n;
}
// end of function average
int main(
)
{
int i, n;
float grades[SIZE]; // array declaration
printf("Enter number of students:
");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter grades for %d students
:", n);
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
} // end of
for
printf("The Average of grade is
%.2f\n", average(grades, n));
//
Note: function call in a printf statement
return 0;
}
// emd of main
Sample Output:
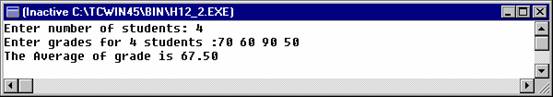
Solved Problem #4:
·
To
pass the array to a function we write the name of the array.
·
To
declare the function that accepts an array as its parameter we write the name
of the array followed by the [ ] without the size of the array in its
parameter declaration part.
·
Consider
the following problem of finding the maximum of 4 integer numbers.
#include
<stdio.h>
#define SIZE 4 // defining
the size of the array as 4.
int max (int
arr[ ] ) ; // declaring the function max
which
// returns integer value and accepts an
integer array called arr
void main
(void)
{ int arr [SIZE] , j , big ; // declaring the array arr
// along with other variables
for ( j = 0 ; j < SIZE ; ++j ) //using for loop to read the array
{
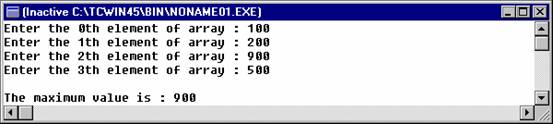
printf ("Enter the %dth element of
array : ", j ) ;
scanf ( "%d", &arr[j] ) ;
} // end of for
big = max ( arr ) ; //calling the function max
// by
passing the array with only name
printf ("\nThe maximum value is :
%d\n", big ) ;
}
// end of main
int max ( int arr[ ] ) // function declaring that it
// accepts integer array arr as its input
{ int
j , big = 0 ;
for ( j = 0 ; j < SIZE ; ++j ) //using for loop to find the
// maximum number in array arr
{
if ( arr[j] > big )
} // end
of for loop
return (big) ; //returning the maximum value
Sample Output: