Computer Engineering Department
Robotics Laboratory
Professor Mayez Al-Mouhamed
Research Theme
A Multi-Threaded Distributed Framework for Telerobotics
Motivation
Approach


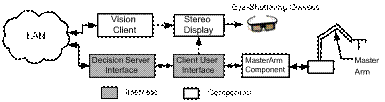
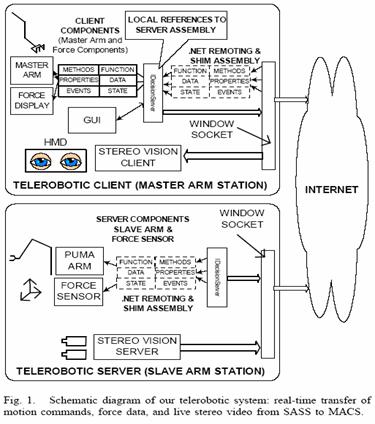
Figure 1: Distributed Component Framework for Telerobotics
1. Software Architecture
o Client-Server Telerobotics and Video Server: Object-Oriented Distributed Component System using Visual C#, .NET Remoting, DirectX, and Windows sockets
o Client (master) and server (slave) interconnected to Internet
o An integrated scheme of client-server components
o Network programming for real-time communication
o Real-time streaming of video data from server to client
o DirectX, COM interfaces for graphic functionalities like DirectShow
o Client support to Augmented Reality (AR) for superimposing graphics
o Support to CAT operability, tool, active compliance at server, indexing, and scalability.
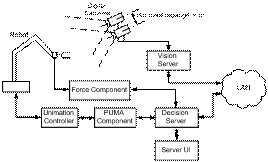
2. Distributed Component System
o Component (PUMA and Force): software proxy (thread) of server
o Public methods, ConnectRobot, InitializeRobot, Move, etc.
o Cartesian motion mapping at tool and world frames
o Public properties, Booleans for robot state, and Public Events
o Communication and synchronization mechanisms.
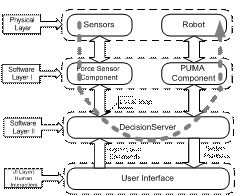
3. Multi-threaded Execution
o Simultaneous activation of many threads like
o Thread Pipelining: Grabbing of two digital cameras at server
o Communication thread: Transfer of video from Server to client
o Force Thread: Streaming of Force from server to client operator hand
o Command Thread: Rendering hand motion and transfer to server
o Network sharing: Video Server and the Distributed Component
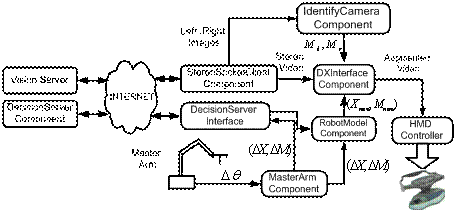
4. Multi-threaded Execution
o DecisionServer component provides slave supervisory control
o Server Side Interfaces and .NET Remoting
o A component has a set of public methods, properties, and events
o Interfaces serve as a contract for any component which implements the interface.
o Shim Classes hide component assembly to increase security
o IProxyRobot and IForceSensor to communicate with PUMA and Force Sensor components
o IDecisionServer inherits both of the above interfaces
.NET Remoting publishes an instance of DecisionServer component on the network
o Allows defining a unified set of methods, properties, and events within DecisionServer component
o .NET Remoting enables access to remote objects using SOAP.
5. Overall
o A reliable and efficient man-machine interface between a Server Station (Slave) and a Client Station (Master) over the Internet
o OO distributed component framework:
o Software reusability, ease of extensibility, debugging, and data Encapsulation
o Automatic handling of network resources and data transfer (.NET remoting)
o Isolation of components from network protocol issues
o Enhances data security as well as facilitates deployment
o Stereo vision support, DirectX and Hardware Accelerated Graphics APIs
o Multi-threaded execution for multi-streaming of force, command, and for live stereo video data transfer