The overall half-life for the multi-step decay process:
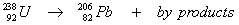
is 4.5 x 10
9 years. What is the age of a rock containing 50.0 mg
of
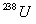
and 24.0 mg of
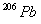
assuming that all the
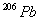
present
was produced by the decay process only? (Hint: determine how many
mg. of
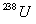
were consumed to produce 24.0 mg of
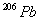
)