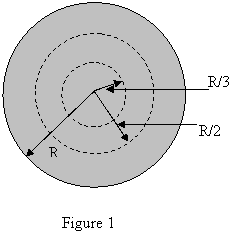
A cylindrical wire of radius R = 2.0 mm has a uniform current
density J = 2.0*10**(5) A/m**2. What is the current through
the portion of the wire between radial distances R/3 and R/2?
(see figure 1)
a 1.95 A.
b 3.73 A.
c 5.31 A.
d 0.35 A.
e 9.11 A.
==============================================
Question 2
A heater element of resistance 10**3 Ohm is constructed
to operate at 110 V. How much thermal energy is produced
in one hour by the heater?
a 4.4*10**4 J.
b 2.2*10**7 J.
c 5.1*10**2 J.
d 6.2*10**5 J.
e 1.9*10**5 J.
==============================================
Question 3
A current of 0.300 A is passed through a lamp for 2.00 minutes
using a 6.00-V battery. The energy dissipated by the lamp during
the 2.00 minutes is:
a 216 J
b 20.0 J
c 36.0 J
d 1.80 J
e 12.0 J
==============================================
Question 4
A copper wire of cross sectional area 3.00*10**(-6) m**2
and length 4.00 m has a current of 2.25 A uniformly
distributed across that area.
How much electric energy is converted to thermal energy
in 10.0 minutes ?
[The resistivity of copper is 1.68*10**(-8) ohm*m]
a 0.50 J
b 68.0 J
c 13.6 J
d 21.7 J
e 30.2 J
==============================================
Question 5
If 4.7*10**(16) electrons pass a particular point in a wire
every minute, what is the current in the wire?
a 2.9*10**(-5) A.
b 1.3*10**(-4) A.
c 4.7*10**(-3) A.
d 2.9*10**(-3) A.
e 9.1*10**(-3) A.
==============================================
Question 6
An electric device, which heats water by immersing a
resistance wire in the water, generates 153 J of heat per
second when an electric potential difference of 12 V is
placed across its ends. What is the resistance of the
heater wire?
a 0.81 Ohms
b 0.58 Ohms
c 0.94 Ohms
d 2.10 Ohms
e 0.48 Ohms
==============================================
Question 7
At T = 20 degrees-C, the length of a wire is 10 m, and its
cross sectional area is 0.50 mm**2. A potential difference
of 1.0 V is maintained across the ends of the wire. The
resistance of the wire changes by 0.30 ohms for a temperature
change of 50 Celsius degrees.
what is the temperature coefficient of resistivity of the wire ?
At T = 20 degrees, the resistivity is 5.0*10**(-6) ohm*m.
a 15*10**(-3) degrees**(-1)
b 15*10**(-4) degrees**(-1)
c 15*10**(-5) degrees**(-1)
d 6.0*10**(-5) degrees**(-1)
e 6.0*10**(-4) degrees**(-1)
==============================================
Question 8
Conduction electrons move to the right in a certain
wire. This indicates that:
a the current density points to the right but
the electric field points to the left.
b the current density and the electric field both
point to the right.
c the current density points to the left but
the electric field points to the right.
d the current density points to the left but
the direction of the electric field is unknown.
e the current density and the electric field both
point to the left.
==============================================
Question 9
A metal wire of resistance R is cut into three equal
pieces that are then connected side by side to form a
new wire the length of which is equal to one-third the
original length. What is the resistance of the new wire ?
a R
b R/3
c 9*R
d R/9
e 3*R
==============================================
Question 10
A copper wire of cylindrical shape has resistance R.
What is the resistance of a second wire, made of the
same material, that is twice as long and has twice the
diameter ?
a R
b 4R
c 2R
d R/2
e R/4
==============================================
Question 11
A copper wire "1" has a length L1 and diameter d1. Another
copper wire "2" has a length L2 and diameter d2. At constant
temperature, the second conductor has smaller resistance if:
a d2 = d1 and L2 > L1.
b d2 < d1 and L2 < L1.
c d2 < d1 and L2 = L1.
d d2 > d1 and L2 > L1.
e d2 > d1 and L2 < L1.
==============================================
Answers
1 d
2 a
3 a
4 b
5 b
6 c
7 d
8 e
9 d
10 d
11 e