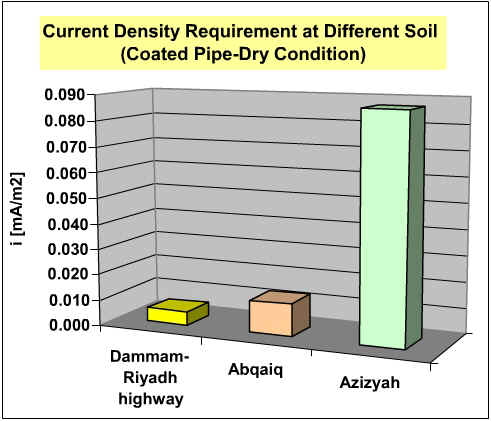

It is observed that the current density required for cathodic protection is higher in a more corrosive environment than in a less corrosive environment.
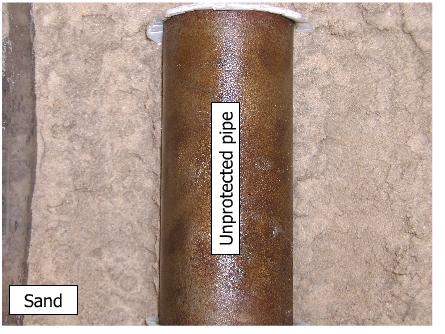
Corrosion in an unprotected pipe is shown below.
|
|
|
|
12. Lab Experiment to Demonstrate Measurement of Current Density For Cathodic Protection of Pipe |
|
| Objective | To demonstrate the measurement of current density for cathodic protection of pipe. |
| Materials | Cu-CuSO4 Reference electrode |
| Digital voltmeter (One for potential measurement and other for reading current) | |
| Variable DC power supply | |
| Pipes (coated and uncoated) | |
| Different types of soils | |
|
|
|
| Procedure |
Connect
digital multimeter (for measurement of current) with negative terminal
of power supply.
Connect
the buried pipe with the digital voltmeter in series. Connect ground bed with positive terminal of power supply. Connect reference electrode with the positive terminal digital voltmeter used for measurement of potential and the buried pipe with the negative terminal. Switch on the power supply and increase the output voltage until the voltage reaches to nearly -0.850 V vs Cu-CuSO4. Tabulate the value of current and potential. The recorded value of current density are shown in Table 1 below. |
Table 1: Current density required on model for cathodic protection.
|
Soil
Source |
Pipe
Condition |
Soil
Condition |
Pipe/Soil
Potential [volt] |
Ia
[mA] |
A[m2] |
Im[mA/m2] |
|
Dammam-Riyadh
Highway |
Uncoated |
Dry |
-0.850 |
0.011 |
0.0569 |
0.193 |
|
Moist |
-0.850 |
0.747 |
0.0560 |
13.128 |
||
|
Coated |
Dry |
-0.850 |
0.0003 |
0.0573 |
0.005 |
|
|
Moist |
-0.850 |
0.004 |
0.0573 |
0.070 |
||
|
Abqaiq
|
Uncoated |
Dry |
-0.850 |
0.037 |
0.0569 |
0.650 |
|
Moist |
-0.850 |
1.122 |
0.0569 |
19.719 |
||
|
Coated |
Dry |
-0.850 |
0.00072 |
0.0573 |
0.013 |
|
|
Moist |
-0.850 |
0.006 |
0.0573 |
0.105 |
||
| Azizyah |
Uncoated |
Dry |
-0.850 |
0.181 |
0.0569 |
3.181 |
|
Moist |
-0.850 |
1.339 |
0.0569 |
23.533 |
||
|
Coated |
Dry |
-0.850 |
0.005 |
0.573 |
0.087 |
|
|
Moist |
-0.850 |
0.0079 |
0.0573 |
0.138 |
|
Figure below show the current density
requirements for coated pipe in different locations in dry and moist
conditions.
|
|
| Conclusion |
It is observed that the current density required for cathodic protection is higher in a more corrosive environment than in a less corrosive environment. Corrosion in an unprotected pipe is shown below.
|
|
|