| Objective | To demonstrate the development of corrosion in crevices because of oxygen concentration differential. |
| Materials | One strip of stainless steel ( 2 x 8) |
| Two pieces of wood ( 0.125 x 0.5 x 1) | |
| One rubber band, 0.125wide and sufficiently long to stretch to 8 | |
|
One Plexiglas rectangular container (4 x 10) |
|
| 3.5% Na Cl solution | |
| 5% Ferric chloride solution | |
|
|
|
| Procedure |
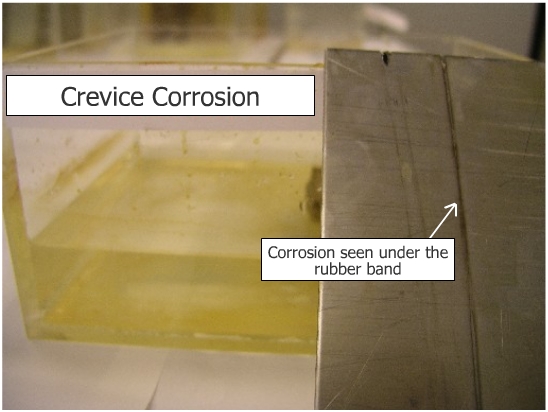
Fill the Plexiglas rectangular container with 3.5% sodium chloride
solution and add few ml of the Ferric chloride solution, then place
the rubber band around the stainless steel specimen so that it is
parallel to the long dimensions of the sample.
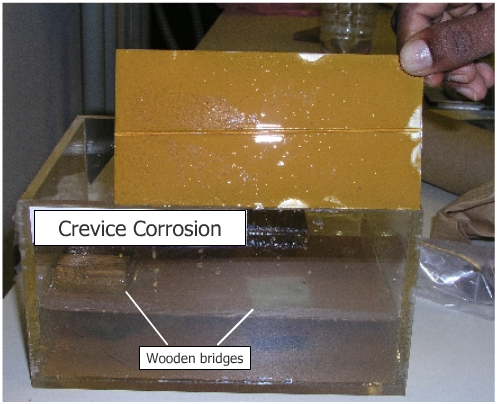
Place wood bridges under the rubber band and on each side and at the
center of the specimen. This will create a crevice at the ends of the
specimen under the rubber band but not on flat surface. Suspend this
assembly in the solution so that the lower edge does not rest on the
bottom of the container and observe this over a period of 6 to 8
weeks.
Observe development of localized corrosion in the area where the rubber band is in contact with stainless steel. Crevice corrosion is caused basically by formation of differential aeration cell. The formation of crevices leads to pitting. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Conclusion |
Crevice corrosion is caused by the formation of crevices between similar materials or between metals and non conductors. |