
| 8. Prevention by Design | |
|
8.6 Areas Requiring Consideration at Design Stage |
|
1. Bimetallic Contact
(a) Potential Difference
The greater the difference of potential between the two metals, the greater is the magnitude of bimetallic corrosion. Figure shows a valve from a condensate pipe. The cast iron valve was incorporated in AISI 304 stainless steel condensate pipe of a copper heat exchanger. The difference of potential between copper, steel, and cast iron caused bimetallic corrosion.

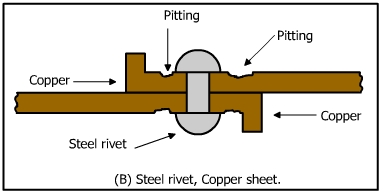
b) Anode to Cathode Area Ratio
A smaller anode area to a large cathode area causes serious bimetallic corrosion because of a large current density on a smaller anodic area. Figure (A) shows a copper rivet in steel sheet and Figure (B) shows steel rivet in a copper sheet. More severe corrosion is observed in the second case.
 |
 |
|
|