|
|
 |
| 5. Cathodic Protection | |
|
5.3 Cathodic Protection Systems [2/8] |
|
Galvanic anodes
Following are the characteristics of the galvanic anodes commonly used.
Table 5.1: Characteristics of Galvanic Anodes
| Metal | Atomic Weight | Equivalent Weight |
Theoretical current output amp/hr/lb (amp/hr/kg) |
| Magnesium | 24.3 | 12.15 | 1000 (2200) |
| Zinc | 65.4 | 32.7 | 372 (820) |
| Aluminum | 27.0 | 13.5 | 1300 (2970) |
The efficiency of magnesium anodes is about 50% , the current output is 500 amp/hr/lb. Zinc oxide operates at an efficiency of 90% and its current output is 335 amp/hr/lb. The efficiency of aluminum anode is about 75% and its current output is 1000 amp/hr/lb.
Typical compositions of magnesium and zinc anodes are given in the following tables.
Table 5.2: Composition of Magnesium Anode
| Element | Percentage (%) |
| Aluminum | 0.010 max |
| Manganese | 0.50 to 1.3 |
| Copper | 0.02 |
| Iron | 0.03 |
| Nickel | 0.001 |
| Other metallic elements | |
| each | 0.05 |
| total | 0.30 |
| Magnesium | - Balance - |
| Zinc | 65.4 |
Some samples of commercially available Magnesium anodes.
|
|
 |
Table 5.3: Composition of Zinc Anode
| Element | Percentage (%) |
| Aluminum | 0.005 max |
| Cadmium | 0.003 |
| Iron | 0.001 |
| Lead | 0.003 |
| Zinc | - Balance - |
Some samples of Zinc anodes.
|
|

|
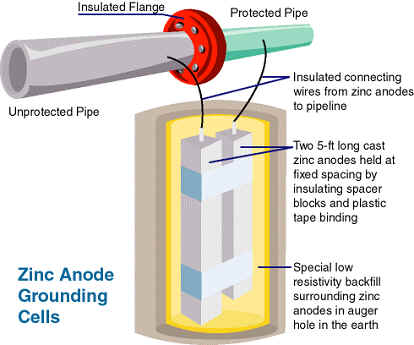
Detailed components of Zinc sacrificial anode. |
|
Table 5.4: Composition of Aluminum Anode
| Element | Percentage (%) |
| Silicon | 0.11 |
| Iron | 0.08 max |
| Zinc | 0.45 |
| Mercury | 0.045 |
| Copper | 0.006 |
| Aluminum | - Balance - |
Some samples of Aluminum anodes.
|
|
 |
Magnesium and zinc anodes are available in many sizes, weights and shapes from the manufacturers. Packaged anodes (anode and backfill furnished as complete unit) are standards with most suppliers. Different anode compositions are used for soil and sea water.
The potential of aluminum anode is -1.65 V and the rate of consumption is 6.8 lb/amp/year.
|
|