f5. Write the particular solution after finding the
coefficients
Define the coefficient as solved for in the previous
step.
Place the equations of the system above in a vector
and use the "solve" command to find the coefficients.
Equate similar terms to find the linear system involving
the undetermined coefficients. This step has to be
done manually.
To make it easy to compare similar terms, use the command
"collect" on the variable x. This will rearrange
the terms as a polynomial in x
Substitute yp
(x) and its derivatives in the differential equation
and evaluate symbolically.
f4. Substitute yp
and its derivatives in the nonhomogeneous equation,
simplify, and equate similar terms to determine the
coefficients
Define the second derivative as
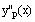
(
use literal subscripts)
and evaluate symbolically.
Define the first derivative as y'p
(x) (use literal
subscripts)
and evaluate symbolically to display the computed derivative.
f3. Compute the first and second derivative of yp(x)
Define the particular solution as
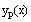
using capital letter A, B, C.. (as needed) for the undetermined
coefficients.
Use literal
subscripts for
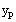
f2. Write the modified form of the particular solution
yp(x)
f1. Write the unmodified form of the particular solution
(skip)
f) Use following steps to find the general solution
of the nonhomogeneous equation using the method of
undetermined coefficients:
e) Give the interval over which the two solutions
of the homogeneous equation are linearly independent
(skip)
Compute the determinant of W(x) to find the Wronskian
of the two solutions. Use the "simplify"
command to simplify the result.
Define the Wronskian matrix as W(x) and evaluate symbolically
to display the results.
Define the two solutions as y1
(x) and y2(x)
in terms of the roots r1
and r2
, then use the symbolic evaluation to display the two
solutions. Use literal subscripts for y and vector subscripts for r.
d) Show that the two solutions of the homogeneous
equation are linearly independent. Justify your answer (skip the justification)
Define the complementary solution as
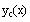
and evaluate symbolically to display the solution with
the roots substitutedby Mathcad.
Use literal subscripts for 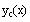 and the arbitrary constants.
and the arbitrary constants.
c) Write the complementary solution
Display the roots.
Use vector subscripts for r.
Define r as the auxiliary equation and use the "solve"
command to find the roots. This way the results will
be assigned to r as a vector and the solutions can
then be referred to using vector subscripts of r.
b) Find the roots of the characteristic equation
_____________O____________
Substitute in the left-hand side of the differential
equation and use the "expand" command. The
answer should be equal to the right-hand side of the
differential equation.
Define y'(x) and y''(x) as the first and second derivative
of y(x), respectively and evaluate symbolically to
see the computed derivatives.
Check if you got the right answer as follows:
Display the general solution. This will give the particular
solution with the constants substituted in the general
solution.
Redefine the general solution in terms of
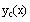
and
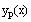
(for the same reason as above.)
Redefine the complementary solution as you did in part
(c). This is required by Mathcad since the earlier
definition of
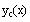
was given before the c's were defined.
g7) Substitute the above values in the general solution
of the nonhomogeneous equation to obtain the particular
solution
Define
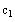
and
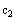
based on the solution found in the previous step.
Use literal
subscripts.
g6) Give the values of the constants c1 and c2 found
above
g5) Compute the reduced row echelon form of the augmented
matrix to solve the system
g4) Form the augmented matrix of the system above
g3. Write the linear system obtained in parts (g1) and
(g2) as a matrix equation A c = b
(skip)
Evaluate the first derivative at the initial point and
set it equal to the given initial value, then evaluate
symbolically to get the second equation of the linear
system.
Define the derivative of y(x) as y'(x) and evaluate
symbolically.
g2. Compute the first derivative of the general solution
in part f6 and apply the second initial condition
Evaluate y(x) at the initial point and set it equal
to the initial value, then evaluate symbolically to
get the first equation of the linear system involving
the arbitrary constants.
g1. Apply the first initial condition on the general
solution in part f6.
g) Use the following steps to find a particular
solution of the nonhomogeneous equation satisfying
the given initial conditions:
Define the general solution y(x) as the sum of the complementary
solution and the particular solution and evaluate symbolically
to display the result.
f6. Write the general solution of the nonhomogeneous
equation
Redefine the particular solution (you may copy it from
step (f2)) and evaluate symbolically to display the
result.
Note: This redefinition is required by Mathcad so that
it can substitute the values of the coefficients.
Statement of the problem:
Use the method of undetermined coefficients to solve
the given initial value problem.
Each student is assigned a different problem. From the
list of problems below, select the problem with a number
matching your class list number.
Vector Subscripts
Keystroke: [
To type a vector subscript like
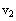
1. Type the vector name (v)
2. Type [ (left bracket). The insertion point extends
down for typing subscripts
3. Type the subscript (2).
4. Press the spacebar once to get out of subscript
mode.
This will refer to the 2nd element of vector v. (provided
that the origin is set to 1, otherwise it will refer
to the third element of v).
Literal Subscripts
keystroke: period
To type a literal subscript like
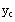
1. Type the first part of the name (y)
2. Type a period. The insertion point extends down
half a line.
3. Type the second half of the name, the part you want
as a subscript (c)
4. Press the spacebar once to get out of subscript
mode.
Be sure not to confuse literal subscript with array
subscripts . Although they appear identical, they are
quite different. Literal subscripts are viewed as an
extension of the variable name, while vector subscripts
are used to refer to elements of vectors (see below).
Remarks:
This computer project is based problem 1 of major exam
2. The problem was designed and solved (see solution
of major exam 2) so that it can be used as a template
for this project.
Some steps given in the solution of the exam problem
are omitted in this project. However, to keep a matching
reference to the step, they are marked with the word
"skip."
Instructions and comments are given for each step of
the solution. Some instructions are placed in the middle
to tell you that the computational result will be long
and will require an entire line to display. Thus, you
should start typing below the given instruction rather
than beside.
Mathcad has two types of subscripts: Literal subscripts
and Vector vector subscripts. The difference is explained
below. You will be guided as to when to use one or
the other.
Instructions
Carefully fill out the personal information at the top
of this worksheet.
Before you start working on the worksheet, use the "save
as" command to save the
worksheet with the
following name:
SxxLyyCP
.mcd
where, xx is your section
number
yy is your class list
number
T
o facilitate the grading of the project, be as neat
as possible and place your input in the space provided
for you.
Unless absolutely necessary, do not add or delete lines
into the document. Enough room is given for writing
your answers.
If for some reason the screen display gets missed up,
press Ctrl+R to refresh the screen.
Frequently save your worksheet to avoid losing your
work.
If you need help with the project or the course material,
e-mail me a short description of the problem and I
will try to help as soon as possible.
You should submit the project on or before Monday January
10, 2005.
e-mail
your worksheet named as explained in part (2) above
to:
afarahat@kfupm.edu
.sa
Do
not send a zipped file.
a) Write the associated homogeneous equation (skip)
Copy the given initial conditions and paste them here.
satisfying the initial conditions
Copy the differential equation you are supposed to solve
from the list of problems given above and paste is
here.
1.
Execute the following steps to find a solution to the
differential equation
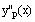 (use literal subscripts)
and evaluate symbolically.
(use literal subscripts)
and evaluate symbolically.