Best of Hubble
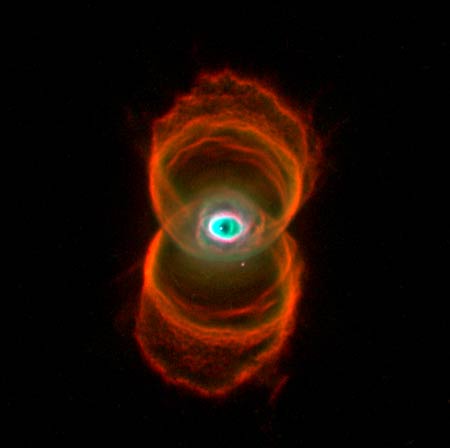
Hourglass
Nebula
This
image shows a planetary nebula. A sun-like star has undergone "death
tremors" at the end of its life. The star had difficulty in getting enough
fuel to keep up its nuclear furnace, and has now shed off some of its surface
material in two directions.
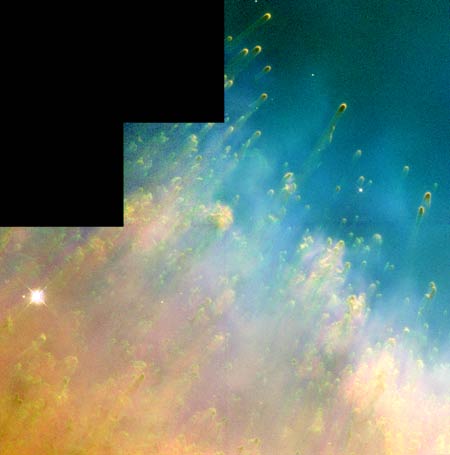
The
Helix Nebula
A
doomed star in the center of the Helix nebula (outside the image in the
direction of the upper right corner), is spewing out hot gas and energetic
radiation. Collisions with colder gas creates dense knots with long comet-like
tails. The colder gas has been ejected from the dying star some 10.000 years
ago.
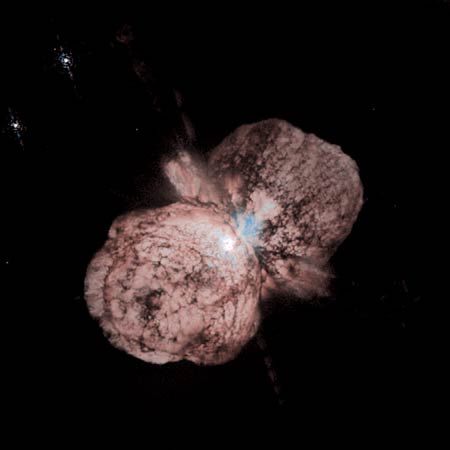
The
Eta Carinae Nebula
The
massive star Eta Carinae (almost hidden in the center) underwent a giant
explosion some 150 years ago. The outburst spread the material that is visible
today in this very sharp Hubble image.
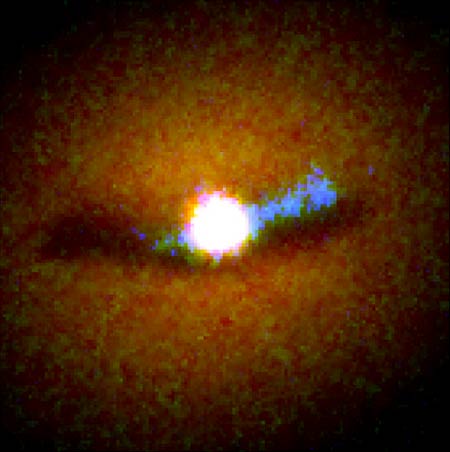
Black
Hole Surroundings
At
the center of a galaxy a black hole is peeping out over the edge of a swirling
dusty disk.Here all kinds of material - dust, gas and even stars - are steadily
falling into the violent black hole, thereby creating a blaze of energetic
ultraviolet light (coloured blue in the picture).

Saturn
- the Ringed Planet
The
ring swirling around Saturn consists of chunks of ice and dust.Saturn itself is
made of ammonia ice and methane gas. The little dark spot on Saturn is the
shadow from Saturn's moon Enceladus.
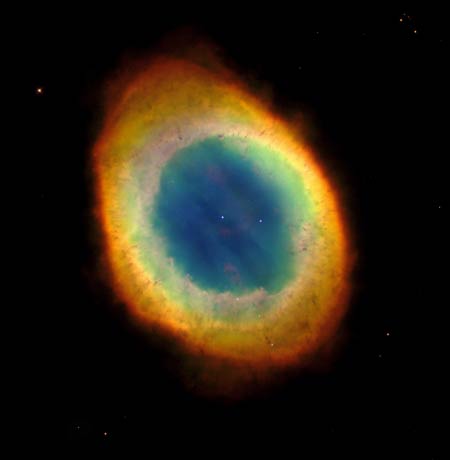
The
Ring Nebula - M57
One
of the most famous of all planetary nebulae. A dying star has thrown off some of
its outer material thousands of years ago. The nebula is situated 2.000 light
years away in the constellation Lyra.
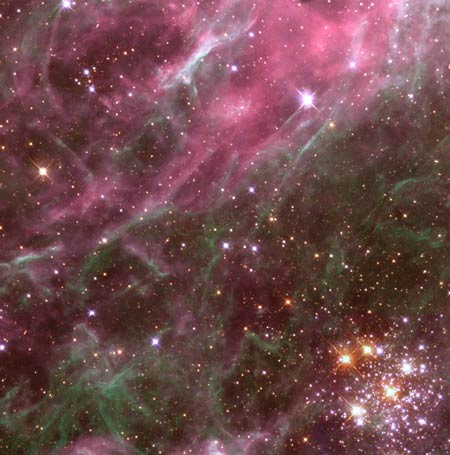

Hodge
301 in the Tarantula Nebula
The
star cluster Hodge 301 is an old cluster. Many of its stars have already
exploded as supernovae. The filaments in the upper left corner have been
compressed by the explosions of these stars. Elsewhere in the picture news stars
are being born.
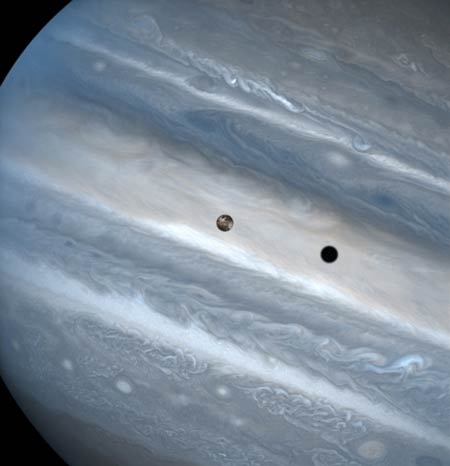

Jupiter
and the Shadow of Io
Jupiter's
moon Io and its shadow are hurling across the face of the biggest planet in our
Solar System. Io itself is a very interesting moon, well known for its many
active volcanoes.

NGC
2440
NGC
2440 is a planetary nebula ejected by a dying star. The nebula is rich in clouds
of dust, some of which form long, dark streaks pointing away from the central
star. In addition to the bright nebula seen here, NGC 2440 is surrounded by a
much larger cloud of cooler gas.
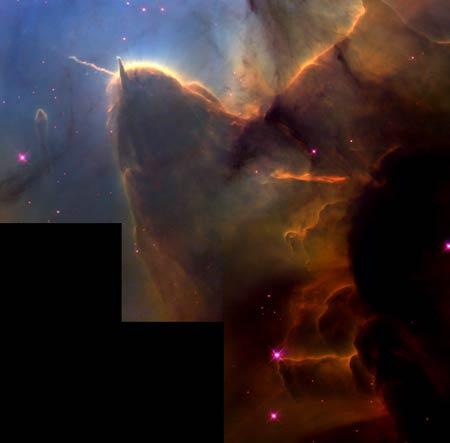

The
Trifid Nebula
Massive
newborn stars are creating in this dramatic torn apart image of the Trifid
Nebula.The Trifid Nebula is home to many thousands of newly created stars. The
source of the jet is a young very hot star buried in the cloud.
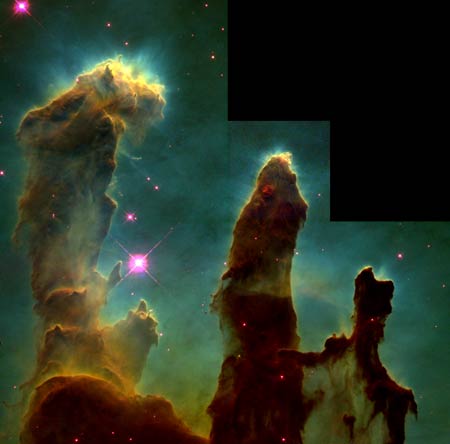

The
Eagle Nebula, M16
These
columns that resemble stalagmites protruding from the floor of a cavern columns
arein fact cool interstellar hydrogen gas and dust that act as incubators for
new stars. Inside them and on their surface astronomers have found knots or
globules of denser gas. These are called EGGs (acronym for "Evaporating
Gaseous Globules"). Inside at least some of the EGGs stars being formed.
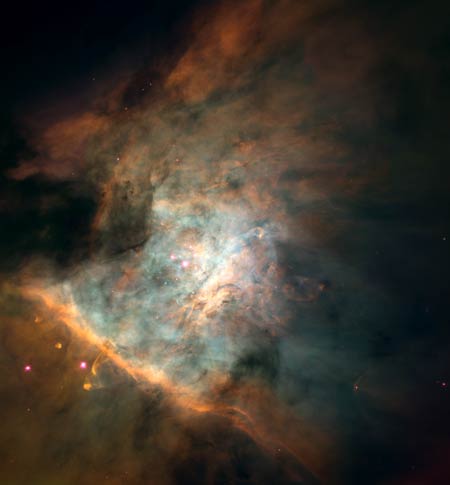

The
Orion Nebula
A
stunning picture of the most famous stellar factory. In the Orion Nebula
hundreds of stars are being born, or are in the early stages of their infancy.
Most fascinating is the discovery of small planetary systems being formed around
some of the stars in this nebula.
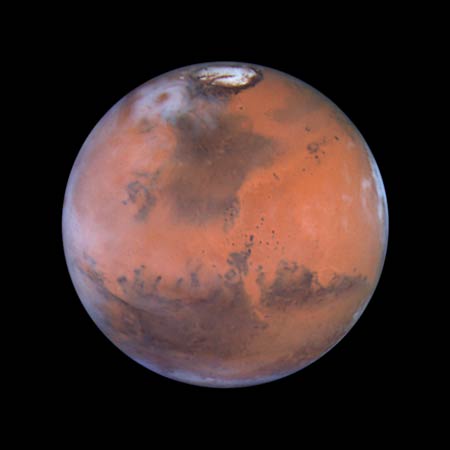

Mars
At
a distance of 87 million kilometres Hubble has captured this sharp image of our
neighbouring planet in the Solar System. The red colour of the martian surface
is due to 'rusted' iron-composites.
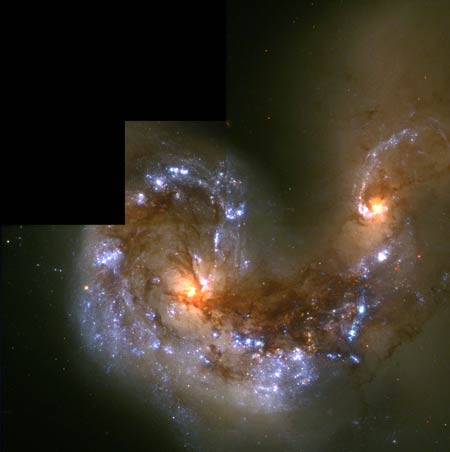

Antennae
Galaxies Colliding
Two
galaxies are colliding in a massive clash. The shock from the collision is
creating thousands of new bright star clusters seen as blue spots all over the
picture. The centres of the two galaxies are orange due to the older, cooler -
and thus more red - stars there.

Spiral
Galaxy NGC 4414
This
magnificent image of a spiral galaxy shows how these galaxies have central
regions containing older and more red and yellow stars. In the spiral arms,
stars are being born all the time, and therefore these arms contain more blue
stars - and also large amounts of dust.
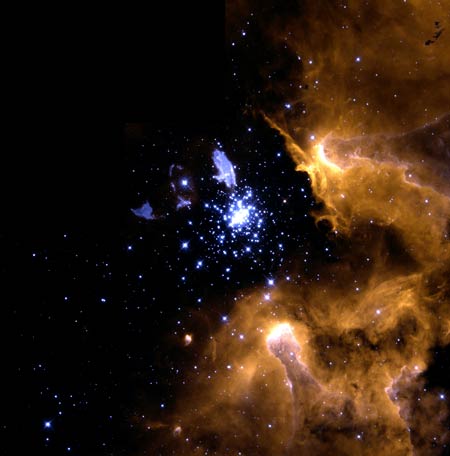

NGC
3603
The very energetic radiation from young hot stars in the star cluster NGC 3603 is bursting into colder gas and dust making the gas glow. The radiation from the stars has blown a "bubble" around the cluster free from gas.