Calculate the amount of energy, in Joules, required to
completely melt 130 g of lead initially at temperature of
15.0 degrees Celsius. Melting point of lead = 328 degrees
Celsius, latent heat of fusion of lead = 2.32*10**4 J/kg
and the specific heat of lead = 128 J/kg/K.
a 1.31*10**4.
b 8.25*10**7.
c 3.02*10**3.
d 5.21*10**3.
e 8.22*10**3.
==============================================
Question 2
Two moles of a monatomic ideal gas at a temperature of 300 K
and pressure of 0.20 atm is compressed isothermally (constant
temperature) to a pressure of 0.80 atm. Find the work done by
the gas.
a 0 J
b +6900 J
c -6900 J
d +18000 J
e -18000 J
==============================================
Question 3
On a cold winter day, metallic objects generally feel
cooler to the touch than wooden objects.
This is because:
a the equilibrium temperature of metal is lower than
that of wood.
b the mass density of wood is less than the mass
density of metals.
c a given mass of wood contains more heat than the same
mass of metal.
d metals conduct heat better than wood.
e heat tends to flow from metal to wood.
==============================================
Question 4
A steel washer (ring) has an inner diameter of 4.000 cm and
an outer diameter of 4.500 cm at 20 deg C. To what temperature
must the washer be heated to just fit over a rod that is
4.010 cm in diameter?
(Coefficient of linear expansinon of steel, alpha,
= 11*10**-6 per C deg)
a 315 deg C
b 247 deg C
c -40 deg C
d 100 deg C
e 509 deg C
==============================================
Question 5
Gas within a closed chamber undergoes the cycle shown in
Fig. 2. Calculate the net heat added to the system in a
complete cycle.
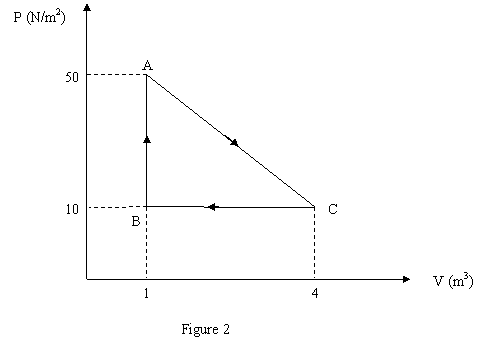
a 14 J.
b 31 J.
c 10 J.
d 73 J.
e 60 J.
==============================================
Question 6
A metal rod has a length of 10.000 cm at 20 degrees-C,
and a length of 10.025 cm at the boiling point of water.
What is the temperature if the length of the rod is
10.015 cm ?
a 68 degrees-C
b 70 degrees-C
c 74 degrees-C
d 50 degrees-C
e 56 degress-C
==============================================
Question 7
A room has a window made of two layers of glass separated
by an air layer as in figure 4. Each of the 3 layers has
a thickness of 0.50 mm and an area of 1.0 square meter.
The temperature outside the room is - 20 degrees-C, while
the temperature inside the room is + 20 degrees-C.
What is the rate of heat transfer by conduction through
the window ? Assume steady state.
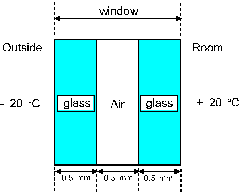
a 1.0 kW
b 2.0 kW
c 0.90 kW
d 1.2 kW
e 1.4 kW
==============================================
Question 8
A cylindrical copper rod of length 1.5 m and cross section
6.5 cm**2 is insulated to prevent heat loss through its surface.
The ends are maintained at a temperature difference of
100 C deg by having one end in a water-ice mixture and the
other in boiling water and steam. How much ice is melted per
hour at the cold end?
(thermal conductivity of copper, kappa, = 401 W/(m.K);
heat of fusion of ice, Lf, = 333*10*3 J/kg )
a 980 g
b 469 g
c 330 g
d 188 g
e 281 g
==============================================
Question 9
In an insulated container, 250 grams of ice at
0 degrees-C are added to 500 grams of water at
18 degrees-C.
How much ice remains when the system reaches equilibrium ?
[The latent heat of fusion of water = 333 kJ/kg and
the specific heat of water = 4190 J/kg.K].
a 79.0 g
b 113 g
c 250 g
d 137 g
e 300 g
==============================================
Question 10
Liquid nitrogen boils at temperature of -196 degrees Celsius
when the pressure is one atmosphere. A silver coin of
mass 1.5*10**(-2) Kg and temperature 25 degrees Celsius
is dropped into the liquid. What mass of nitrogen boils
off as the coin cools to – 196 degrees Celsius.
[Take the specific heat of silver = 235 J/Kg/K and latent heat
of vaporization for liquid nitrogen is 2.0*10**5 J/Kg.
a 3.90 g.
b 89.0 g.
c 20.1 g.
d 8.10 g.
e 112 g.
==============================================
Question 11
A system undergoes an adiabatic process in which its
internal energy increases by 20 J. Which of the following
correctly describes changes in the system ?
a Heat: 20 J removed, Work: none
b Heat: none, Work: 20 J on the system
c Heat: 20 J added, Work: none
d Heat: none, Work: 20 J by the system
e Heat: 40 J added, Work: 20 J by the system
==============================================
Question 12
A 200-g copper piece was initially at a temperature of
325 degrees-C. It is then dropped into 2000 g of water
at a temperature of 5 degrees-C. Assuming that the
copper-water system is an isolated system, and the
water does not vaporize, find the heat gained by water.
The specific heat of copper is 0.0923 cal/g.K
The specific heat of water is 1.00 cal/g.K.
a 5850 calories
b 16000 calories
c 4600 calories
d 12200 calories
e 9500 calories
==============================================
Question 13
How much heat is required to melt ice of mass 500 g at -10
deg C to water at 0 deg C?
(specific heat of ice, c, = 2220 J/(kg.K);
heat of fusion of ice, Lf, = 333*10*3 J/kg )
a 8.45*10**5 J
b 2.05*10**5 J
c 9.05*10**5 J
d 1.78*10**5 J
e 3.01*10**5 J
==============================================
Question 14
A rod is made of two different metals, one piece has
length L and thermal conductivity K and the other piece
has a length 2 L and thermal conductivity 3 K. The rod
is situated between two heat reservoirs as shown in
Fig. 1. What is the steady state temperature at the
interface of the two pieces ?
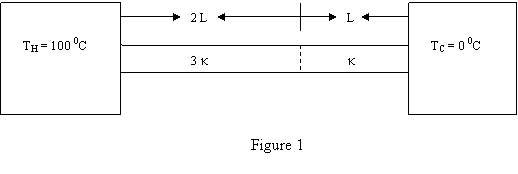
a 35 Kelvin.
b 68 Kelvin.
c 60 Kelvin.
d 0 Kelvin.
e 333 Kelvin.
==============================================
Question 15
An ideal gas is taken through the cycle ABCA, shown in
figure 4. The work done along the paths AB, BC and CA,
are respectively:
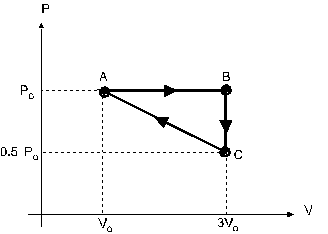
a 2*Po*Vo, Po*Vo, -1.5*Po*Vo
b 2*Po*Vo, zero , +1.5*Po*Vo
c 2*Po*Vo, zero , -Po*Vo
d 2*Po*Vo, zero , -1.5*Po*Vo
e 2*Po*Vo, zero , -2*Po*Vo
==============================================
Question 16
Body A is at a higher temperature than Body B. When they are
placed in contact, heat will flow from A to B
a until both have the same temperature
b only if the volume of A is larger than that of B
c only if A has the greater internal energy content
d only if the specific heat of A is larger that that of B
e only if the thermal conductivity of A is greater than that of B
==============================================
Question 17
A cylindrical glass beaker of radius 1.5 cm contains 20 mL
of water at 5.0 degrees-C. What is the change in the water
level when the temperature rises to 90 degrees-C. Ignore
the change in the volume of the glass beaker.
[The coefficient of volume expansion of water is
2.1*10**-4 (degrees-C)**-1 and 1 mL = 1 cm**3].
a 16 mm
b 0.51 mm
c 0.35 mm
d 0.11 mm
e 360 mm
==============================================
Question 18
When the temperature of a sphere is raised by
75 degrees Celsius the sphere’s volume increases
by 6.9*10**(-5) m**3.If the original volume
is 1.8*10**(-2) m**3, find the coefficient of
linear expansion of the sphere.
a 5.1*10**(-5) (Celsius degrees)**(-1).
b 3.4*10**(-5) (Celsius degrees)**(-1).
c 9.0*10**(-5) (Celsius degrees)**(-1).
d 1.7*10**(-5) (Celsius degrees)**(-1).
e 2.8*10**(-5) (Celsius degrees)**(-1).
==============================================
Question 19
A gas is compressed at a constant pressure of 0.800 atm
from a volume of 9.00 L to a volume of 2.00 L.
In the process, 400 J of heat flows out of the gas.
What is the change in the internal energy of the gas ?
a - 166 J
b - 966 J
c 566 J
d 166 J
e - 566 J
==============================================
Question 20
An aluminum rod and an iron rod, each of length 20.0 cm
and radius 1.00 cm, are placed end to end, as in
figure 3. The sides of the rods are insulated.
The outer end of iron is at 80.0 degrees-C and that
of aluminum is at 20.0 degrees-C. In steady state,
what is the temperature at the junction of the two rods ?
[The thermal conductivity of aluminum = 235 W/m.K and
the thermal conductivity of iron = 14.0 W/m.K].
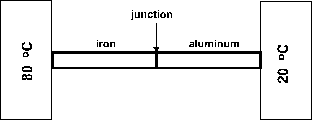
a 76.6 degrees-C
b 15.7 degrees-C
c 50.0 degrees-C
d 85.6 degrees-C
e 23.4 degrees-C
==============================================
Answers
1 e
2 c
3 d
4 b
5 e
6 a
7 b
8 d
9 d
10 a
11 b
12 a
13 d
14 e
15 d
16 a
17 b
18 d
19 d
20 e