Types of
Coating Systems
A coating system may use
different types of pigments depending on their attributes such as their
impermeability, their inhibition capabilities and cathodic protection.
| 1.
Impermeable systems |
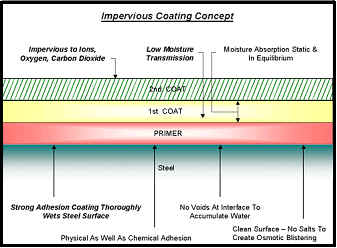
In these systems, the coating
must be impervious to air, oxygen, carbon dioxide as to the penetration of
ionic species. It must have good dielectric properties. A common example
is the application of coal tar enamel. The primer must be impermeable.
|
| 2.
Inhibitive systems
|
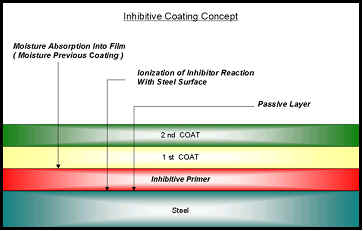
The success of this system
depends on the nature of inhibitive films which absorbs the penetrating
moisture and forms a passive film on the surface, thus blocking any
atmospheric intervention with the substrate to cause corrosion. Red lead
and lead chromates are good examples. These coatings are suitable for
application in the marine, industrial or atmospheric condition.
|
| 3.
Cathodically protective systems |
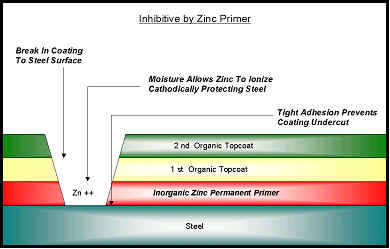
The
success of this system depends on the Zinc primer which are highly adherent to
the surface. The zinc protects the substrate by breakdown, releasing electrons
to the substrate and protecting it. Intermediate and top coats of
polyurethane, or vinyl have been successfully used for protection of
underground pipes.
|
Components
of Coating Systems
The chief components of coating
systems and their functions are:
| 1.Primers |
They provide a strong bond to the substrate
for adhesion. It includes rust inhibitors and wetting agents. They also
provide a compatible base for the top coats. They also prevent
corrosion. |
| 2.
Bodycoats
|
The bodycoats is applied to increase the
total thickness of coating. It provides strong adhesion, strong chemical
resistance and strong bond to primer and top coat. |
| 3. Topcoats |
They provide a sealing for the coating
systems and prevent the ingress of chemicals, water and other corroding
species. They also provide a pleasing color. |
Paints and
Coating Systems Categories
Basically
there are two categories:
-
Convertible
-
Non-convertible
Convertible
paints and coatings: They require a chemical reaction or polymerization
to form the protective coating film. Example: oil based points, alkyd paints,
epoxy coatings, etc.
Non
convertible paints and coatings: A two component paint of polyvinyl
chloride, zinc chromate and phosphoric acid. These coatings are applied to
enhance the adhesion of top coatings.


