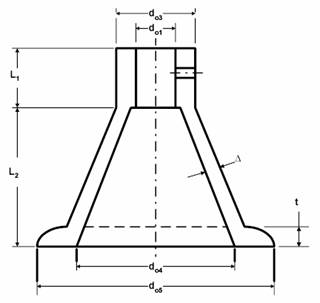
Design of the Body

Select a suitable material for the body from table E-24
When two cylindrical parts are assembled by shrinking or press-fitting one part upon another, a contact pressure is created between the two parts.
A
contact pressure ![]() exists between the members at the transition radius R,
causing radial stresses
exists between the members at the transition radius R,
causing radial stresses ![]() in each member at the contacting surfaces.
in each member at the contacting surfaces.
The tangential stress at the inner surface of the outer member is found to be
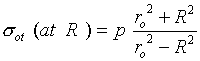 Eqn. ( 3-61 )
Eqn. ( 3-61 )
where
![]() and
and ![]()
Specify a suitable class of force fit from Table 19.6 and get the value of coefficient C from Table 19.7 (Standard Handbook of Machine Design, Shigley, Chapter 19 ).
Calculate the limit, L in thousandths of an inch corresponding to coefficient C and basic size D in inches
![]()
Take the worst case of minimum hole and maximum shaft.
This
will give us the radial interference,
![]() and is the radial deformation which the two members must
experience.
and is the radial deformation which the two members must
experience.
Calculate ![]() using Equ. ( 3-62 )
using Equ. ( 3-62 )
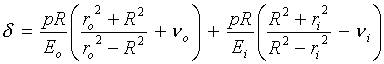 Equ. ( 3-62 )
Equ. ( 3-62 )
where
![]()
The body will also be subjected to compression as well as torsion.
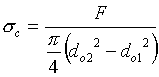
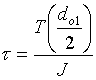 ,
, 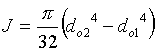
Calculate principal stresses ![]() with
with ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and
![]() .
.
Apply maximum normal stress theory to calculate factor of safety.
Determine the base dimensions
Check base for buckling.
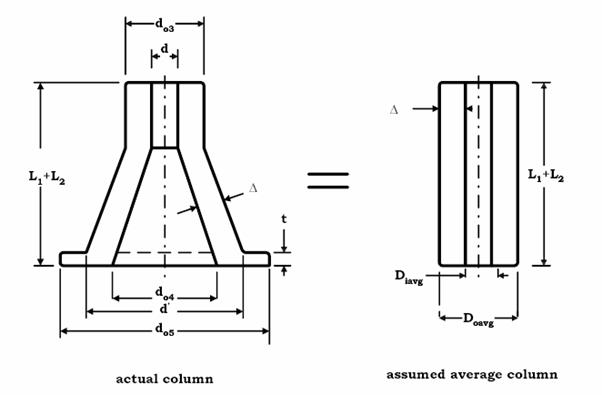
Consider body as an equivalent column of inner diameter,
![]() and outer diameter of
and outer diameter of
![]() .
.
![]() ,
,
![]()
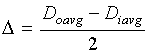
![]()
Calculate ![]() by considering compressive stresses on the equivalent column
by considering compressive stresses on the equivalent column
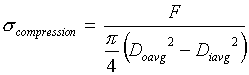
![]()
where
![]() is ultimate compressive strength of the body material.
is ultimate compressive strength of the body material.
Take
length of the column as ![]() .
.
![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Calculate ![]() , where
, where 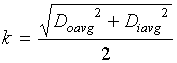 and
and 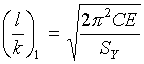
If
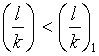 , then it is a Johnsonís column, otherwise Eulerís column.
, then it is a Johnsonís column, otherwise Eulerís column.
Calculate service factor, n. It should be greater than 3.5.
Calculate base seat outer diameter by considering bearing (compression) stress
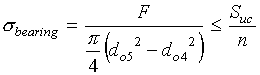
![]()
Determine thickness Ďtí of the base:
Assume a uniformly distributed load over the entire base seat at circumference i.e. at the center
![]()
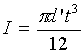 and
and ![]()
![]()
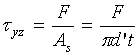
Calculate ![]() and
and ![]() in terms of t.
in terms of t.
Calculate t by applying appropriate failure theory for brittle material.